Appointment
Schedule your consultation with Dr. Abhishek Miryala for expert neurological care.
Working Hour
- 5:30 PM - 8:30 PM
- 5:30 PM - 8:30 PM
- 5:30 PM - 8:30 PM
- 5:30 PM - 8:30 PM
- 5:30 PM - 8:30 PM
- 5:30 PM - 8:30 PM
- Closed
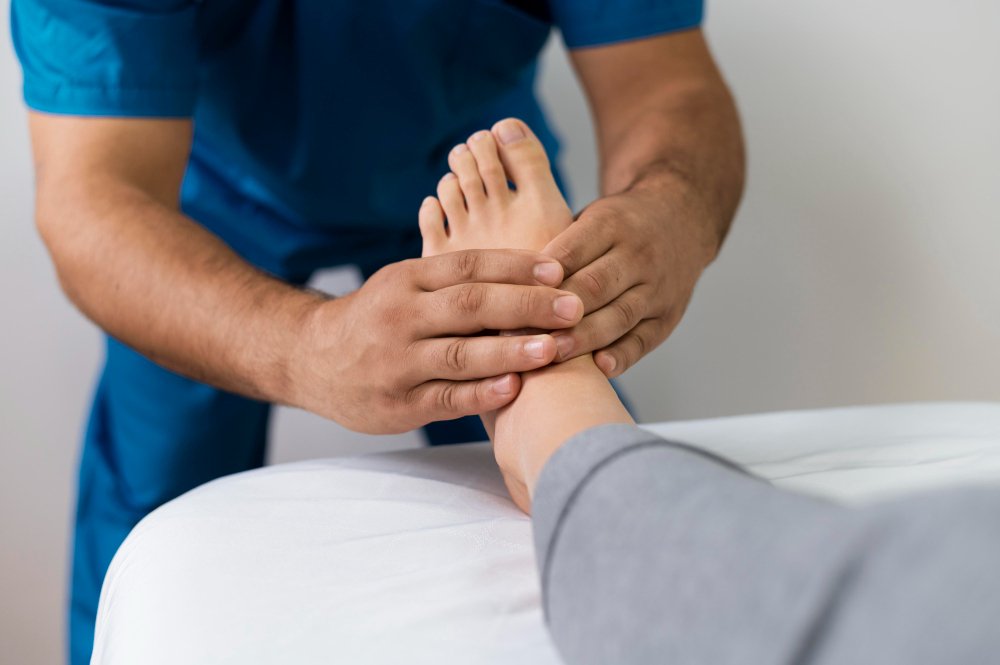
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy refers to damage or dysfunction of the peripheral nerves, which are responsible for transmitting signals between the brain, spinal cord, and the rest of the body. This condition can cause a wide range of symptoms, including pain, tingling, numbness, and weakness in the limbs. Peripheral neuropathy care focuses on identifying the underlying causes, alleviating symptoms, and improving quality of life.
Common Causes of Peripheral Neuropathy
- Diabetes: One of the most common causes, diabetic neuropathy results from high blood sugar levels damaging nerves over time.
- Alcoholism: Chronic alcohol use can lead to vitamin deficiencies and nerve damage.
- Infections: Certain infections, such as shingles or HIV, can affect peripheral nerves.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus can lead to nerve inflammation.
- Chemotherapy: Some cancer treatments, particularly chemotherapy drugs, can cause nerve damage.
- Trauma or Injury: Physical damage to nerves from accidents or repetitive motion can lead to neuropathy.
- Vitamin Deficiencies: Deficiencies in B vitamins, particularly B12, can impair nerve function.
- Other Conditions: Kidney disease, hypothyroidism, and certain genetic conditions can also contribute to neuropathy.
Symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy
- Pain: Sharp, stabbing, or burning sensations, often in the hands or feet.
- Tingling or Numbness: Loss of sensation or a “pins and needles” feeling, especially in the extremities.
- Weakness: Difficulty walking, lifting objects, or performing daily tasks due to muscle weakness.
- Sensitivity to Touch: Even light touch can feel painful or uncomfortable.
- Balance Issues: Nerve damage in the legs and feet can lead to difficulty walking and increased risk of falls.
- Loss of Reflexes: Reduced ability to feel or respond to certain stimuli, like heat or cold.
Treatment Options for Peripheral Neuropathy
- Medications: Pain relievers, anti-seizure drugs (such as gabapentin), antidepressants, and topical treatments can help alleviate pain and discomfort.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises designed to improve strength, coordination, and balance can help restore function and reduce disability.
- Nerve Blocks or Injections: Targeted injections of corticosteroids or local anesthetics may help reduce inflammation and manage pain.
- Nutritional Support: Addressing vitamin deficiencies with supplements, particularly B vitamins, to support nerve health.
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): A therapy that uses low-voltage electrical currents to reduce pain and stimulate nerve function.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Controlling blood sugar levels (for diabetic neuropathy), avoiding alcohol, and making dietary changes to support nerve health.
- Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture or biofeedback can be used in conjunction with medical treatments to manage symptoms.
When to Consult
- Numbness or tingling in hands or feet.
- Muscle weakness or difficulty walking.
- Sharp, burning pain in the extremities.
schedule a consultation today!


